Microsoft, Google, Nvidia, what advances have been made in generative AI in healthcare?
The market for Generative AI is being rewritten as new opportunities spring up. But what is certain is that because of the AIGC boom, another trillion-dollar company is about to be born - as NVIDIA, a provider of core AI computing power, went "All-in-AI" on May 29, its NVIDIA's shares topped $419 on May 31, pushing its market capitalization past a trillion dollars.
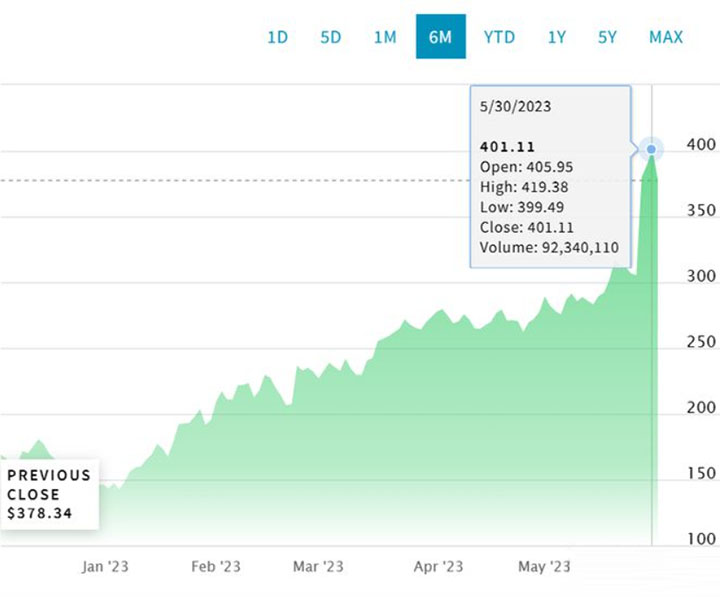
NVIDIA's trillion dollar market cap thanks to its generative AI concept (screenshot from Nasdaq website)
To date, only eight companies in the world have surpassed trillion dollars in market capitalization. Only Apple, Alphabet, Microsoft and Amazon are still ranked above Nvidia in terms of market capitalization.
It is no coincidence that Microsoft, which has also seen another wave of stock price surge recently, is also supported by generative AI - its investment in OpenAI has recently become the key to ignite generative AI with ChatGPT.
After realizing the breakthrough significance of generative AI, the global healthcare industry has rapidly started to introduce generative AI into the healthcare field with unprecedented speed and enthusiasm, and initial results have already been achieved. For reference, Arteries.com has summarized the current cutting-edge cases of global generative AI in healthcare applications.
Microsoft, Google and Nvidia, the big players have their own paths in generative AI+medicine
The biggest news in the exploration of generative AI in healthcare is the cooperation between Epic and Microsoft. As the world's top healthcare information technology giant, EPIC firmly occupies the position of leader in the U.S. electronic medical record (EMR) market, and is also the first choice of large healthcare organizations, and the gap with other competitors is showing a growing trend. According to a KLAS study, EPIC actually lost only once in 2022 out of the 85 public bids it participated in.
At HIMSS23 in April, EPIC announced that it would partner with Microsoft to integrate AIGC into its EHR system. healthcare organizations using Epic's EHR systems will leverage the capabilities of generative AI through Microsoft Azure cloud services in the future - since the release of the GPT-4 model, Microsoft has been rapidly importing services based on the GPT-4 model into its Azure cloud solution.
This is the first time Epic has embraced generative AI, and Epic has now launched two generative-based solutions. One is the introduction of generative AI in the In Basket communications solution, which will automatically draft draft responses for physicians to some of the most common and time-consuming patient messages. Of course, it will not replace the physician's judgment, and the physician can either accept the suggestion or reject it and write it himself.
Epic has already opened a small internal test of the feature, and health care organizations including UC San Diego Health, University of Wisconsin Health and Stanford Health Care have already accessed it for testing, Epic said, adding that the feature will be further expanded for internal testing and may be officially released in a few months once the internal test goes well.
The second option is to combine generative AI with Epic's Slicer Dicker data visualization tool. Previously, users had a high threshold for customizing specific data searches in this tool, requiring a deeper understanding of the data. Generative AI, on the other hand, can automatically suggest different metrics for users based on their input. According to the report, this feature is still under development and is expected to be released later this year.
In March, less than a week before the release of GPT-4, Microsoft's Nuance announced that it would introduce GPT-4 capabilities into its product Dragon Ambient eXperience Express.
Nuance was once the leader in voice AI, not only as the developer of Apple's Siri speech engine, but also once held more than 60% of the global intelligent voice market share. After being challenged by technology giants, Nuance shifted its business focus to the medical field and built a high competitive barrier through several years of deep cultivation.
In April 2021, Nuance was acquired by Microsoft for a huge sum of $19.7 billion. The deal was the third largest acquisition to date and significantly strengthened Microsoft's presence in the healthcare vertical.
Nuance's products focus on speech recognition and transcription services for physicians. Voice AI intelligently recognizes the content of doctor-patient conversations, performs contextual analysis, and subsequently feeds the data into electronic medical records to automatically create clinical records to improve the efficiency of physician diagnosis.
The addition of the GPT model will substantially improve the generation time of clinical records. In general, it takes about four hours to generate clinical records for DAX without the GPT-4 model. Relying on GPT-4's powerful generative big language model and reasoning capabilities, DAX Express reduces this process to just a few seconds.
This dramatically improves the experience for physicians, reduces their paperwork processing burden, makes latency-free clinical records possible, and improves efficiency.
Google, which once led the way in deep learning, still hasn't launched a usable service on generative AI + healthcare, and is half a step behind Microsoft. However, Google also announced in mid-April that it will test its big model specifically for healthcare, Med-PaLM 2, on a limited group of users.
Over the past few years, Google has been working on a medical large language model and released the first generation of Med-PaLM to address the specialization and specificity required in the medical field. the Med-PaLM model has had notable success. It was the first AI to achieve a "passing score" (>60%) on U.S. medical licensing questions, not only answering multiple-choice and open-ended questions accurately, but also providing reasons for its answers and evaluating its own responses.
Med-PaLM 2 went even further. In the medical exam, Med-PaLM 2 was close to the level of an "expert" doctor, scoring 85%. It was also the first AI system to achieve a passing score on the MedMCQA dataset, which includes questions from the Indian AIIMS and NEET physical exams, with a score of 72.3%.
Nonetheless, even the most hardcore Google fan has to admit that Microsoft has indeed jumped the gun on generative AI + healthcare by half a step. However, in this marathon, it is yet to be seen who will have the last laugh.
As the AI core computing power provider, Nvidia relies on the generative AI fire to earn a lot of money. For a long time, Nvidia has been improving its technology and product layout in high-performance computing and data center, and now has a full set of solutions for AI acceleration, occupying 95% of the machine learning GPU market and being almost the only choice for AI big models.
Its data center business revenue has repeatedly increased as a percentage of its revenue. According to its first quarter earnings report, data center business revenue was $4.28 billion, accounting for almost 60% of the company's total revenue; and with 14% year-over-year and 18% year-over-year growth, it is growing quite rapidly.
Nvidia also has a long history of combining generative AI with healthcare, and in 2022, Nvidia is working with King's College London to create a dataset of 100,000 synthetic images of the brain using the Cambridge-1 supercomputer to train AI applications to accelerate understanding of dementia, Parkinson's disease and other brain disorders. The generation logic is similar to that of text, in that real data is split into material and then combined by AI with specific logic to solve the problem of scarce data.
This is not the only case for NVIDIA in synthetic data, as UF Health, an academic health center at the University of Florida, has also partnered with NVIDIA to develop the SynGatorTron generative AI model for generating synthetic clinical data. It is trained based on more than 20,000 patients' decadal data and can synthesize patient profiles that researchers can use to train other AI models in healthcare.
In addition, NVIDIA has partnered with companies such as Alchemab Therapeutics, InstaDeep, Peptone and Relation Therapeutics to help with generative AI for their development of new drugs.
Generative AI is emerging in all areas of healthcare
According to research, the global generative AI market is growing rapidly, with a market size of about $900 million in 2022, expected to reach $1.8 billion in 2023, and $12.1 billion in 2027, representing a compound annual growth rate of 60%. In healthcare, its applications will be spread across drug discovery and development, medical imaging and diagnosis, personalized medical interventions, and automation of hospital and clinical decision support systems.
The generative AI+ healthcare track is also seeing a lot of funding, with conversational bots as the main business Hyro receiving $20 million in Series B funding and healthcare-specific generative AI model development Hippocratic AI receiving $50 million in seed round funding in just the second half of May.
A large number of healthcare startups related to generative AI have also sprung up and started their own "legendary path".
One of Nuance's competitors, Abridge, founded in 2018, has also begun introducing generative AI, which allows Abridge's platform to extract conversation summaries from recordings of patient visits and generate reports. With the use of generative AI, doctors can spend an average of more than two hours less per day on report summaries, according to the report.
Competing with giants like Nuance is obviously not easy, but Abridge has its own unique features - its product is already being used at scale at the University of Kansas Health System. According to reports, more than 2,000 medical staff in the Kansas City area are using the product, which is considered one of the largest current applications of generative AI in the healthcare system.
Abridge is currently integrating its product into electronic medical record systems such as Epic and Cerner. Once the integration is complete, it will provide an optional alternative for healthcare organizations.
Digital platform Doximity has also introduced GPT-based testing capabilities for physicians that can leverage the power of generative AI to streamline time-consuming administrative matters, such as drafting and faxing pre-authorization and appeal letters to insurers.
Syntegra, founded in 2019, on the other hand, has been working on using generative AI to synthesize data since its inception and was one of the first companies to start using generative AI to synthesize data. Generative AI can generate large amounts of synthetic data for data expansion for model training. This will allow developers to explore certain scenarios where data is missing, such as rare diseases or disease areas where data is unevenly distributed.
Syntegra is being tested in collaboration with Janssen Pharmaceuticals, a subsidiary of Johnson & Johnson. Because Syntegra's synthetic data is not subject to the same GDPR as real patient data, it gives the Belgium-based company more freedom in utilizing synthetic data.
The industry generally agrees that generative AI was first used to assist with document generation and synthetic data because they have less direct impact on patients and are relatively low risk. There is a greater risk associated with their use for diagnostic purposes.
It is not difficult to understand that the accuracy of generative AI diagnostics is closely related to the training data, which can result in a false or true output. chatGPT can be a serious nonsense, and Midjourney can output a false or true picture. This should never be allowed in the serious field of health care.
OpenAI, a representative of generative AI, has also specifically pointed out that the output of its ChatGPT based on large language models can be inaccurate, untrue, and sometimes misleading; in addition, ChatGPT can occasionally produce harmful instructions or biased content.
In earlier reports, the GPT-4 scored well on the U.S. SAT and bar exams. According to research published in JAMA, the GPT also gives largely appropriate answers to questions about cardiovascular disease prevention. This does not always occur, however, and according to a recent study published in the American Journal of Gastroenterology, the GPT-3 and GPT-4 failed both the 2021 and 2022 American Gastroenterological Association self-assessment tests.
To pass this test, individuals must score 70% or higher. 65.1% for the GPT-3 and 62.4% for the GPT-4. The study suggests that the GPT's failing scores may be due to the fact that its training data does not include medical journals that require paid access, making the information it knows more outdated and limited.
However, it cannot be denied that generative AI can help physicians answer clinical questions by accessing vast amounts of medical literature and data. Therefore, how to build on the strengths and avoid the weaknesses will be a part of the generative AI applications that will receive a lot of attention in the future. Targeted optimization of models is certainly the most critical step. Google's Med-PaLM for healthcare is based on the generic big model PaLM adapted for the medical field to answer medical questions more accurately and safely.
Babylon, a well-known digital healthcare company, has its famous digital-first "pyramid" system as its core competency. The bottom level of this pyramid is based on a mobile app to enable users to self-manage their health. Users can address most of their needs at this level, including checking symptoms, tracking their health status, managing prescriptions, and accessing clinically relevant guidance.
This tier is critical for Babylon. Through the assessment of digital tools, Babylon can help members understand the current status of their health indicators as well as trends; and, most importantly, risk stratification of the population served. Babylon can then intervene in advance to remind members or set health goals for them to keep them as healthy as possible and prevent their health from deteriorating.
In an interview, Babylon described the proprietary generative AI models it is deploying on its technology platform to support members and healthcare professionals in providing telemedicine consultations to better understand the changing risk profiles of members/patients on our platform to ensure its clinical teams can prioritize the members who need it most.
On the other hand, Babylon has also developed generative AI models optimized for telehealth consultations to automatically summarize consultations between patients and clinicians in near real-time, thereby reducing the administrative burden on clinicians and supporting more targeted consultations with patients.
Babylon also revealed that it is developing solutions to provide predictive insights and care recommendations to its clinical teams in a conversational format through generative AI to support the highest quality of care for patients.
More interestingly, generative AI is bringing scenarios from science fiction movies to real life.
Ten years ago, there was a science fiction movie called "Her". It depicted a thoughtful letter-writer in the not-too-distant future who talks to and eventually falls hopelessly in love with an AI voiced by Scarlett Johansson in order to get over a depressing divorce.
DiagnaMed's just-launched PalGPT.ai almost perfectly replicates this scenario - a generative AI powered by the GPT model that hopes to provide users with an emulated AI companion designed to engage in natural, human-like chats, via text message chat, in order to provide meaningful private conversations, friendly advice and sharing of inner thoughts to improve users' brain health.
PalGPT.ai is built on DiagnaMed's purpose-built CERVAI generative AI platform, on which DiagnaMed plans to build generative AI in multiple segments, with PalGPT.ai as its second commercialized product. Once users sign up for the service, PalGPT.ai will send personalized messages based on their previous interactions, gradually becoming a private space for users to share their thoughts, feelings, beliefs, experiences, memories and dreams.
According to Accenture, 98 percent of healthcare providers and 89 percent of healthcare payer executives believe advances in generative AI are ushering in a new era of enterprise intelligence. Half of healthcare organizations plan to use generative AI for learning purposes, and more than half plan to conduct pilot cases this year. According to the survey, on average, about 40 percent of work time in healthcare could be empowered by generative AI.
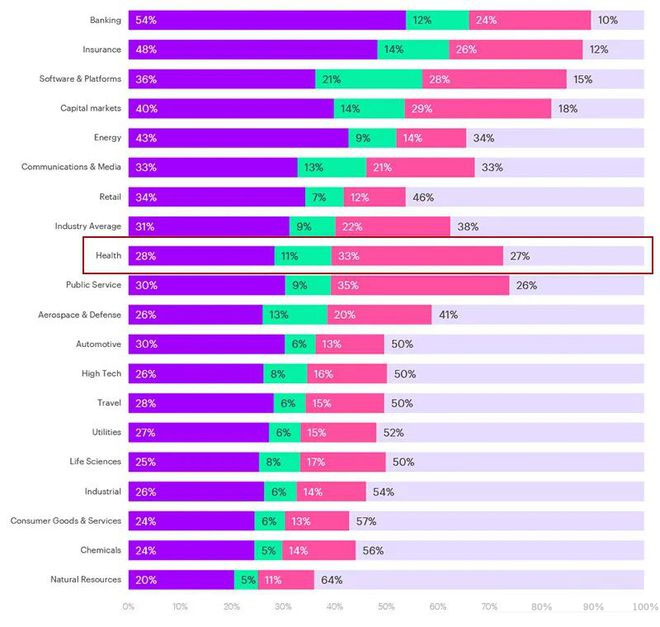
Generative AI will have a huge impact on industries (from Accenture report, with red boxes for healthcare, purple for high potential for automation, green for high potential for enablement, and rose for normal potential for automation and enablement)
For example, generative AI can create value by reducing the amount of time clinicians spend on documentation and allowing them to spend more time with patients, thereby improving staff efficiency, quality and performance. Going forward, we will also continue to monitor the progress of generative AI in healthcare. And how it will change healthcare is something to look forward to for you and me who can grow with the new era.

